

He has experience in range of programming languages and extensive expertise in Python, HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. What's Next?Ībout the author: James Gallagher is a self-taught programmer and the technical content manager at Career Karma. Now you’re ready to start using the git remote add command line operation like an expert!Ībout us: Career Karma is a platform designed to help job seekers find, research, and connect with job training programs to advance their careers.

While Heroku Git is convenient for deployment, it’s not intended to be a stable git repository.
#GIT ADD REMOTE ORGIN CODE#
You deploy your app by pushing its code to a special Heroku-hosted remote that’s associated with your app. If you encounter a “fatal” error when running the command, you should choose a name for your new remote or rename or delete the existing remote with the name you want to use. Git remotes are versions of your repository that live on other servers. The git remote add command allows you to add a remote to a Git repository.
#GIT ADD REMOTE ORGIN FREE#
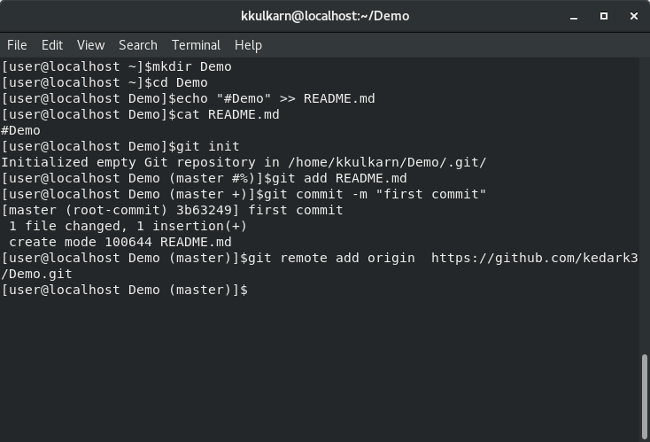
If you are comfortable modifying your existing remote, you can rename or delete the existing remote to free up the name for your new remote. You can resolve this error by using a different name for your new remote. This error is raised when you try to assign a name to a remote that has already been used inside a local version of a repository. You may have encountered an error “fatal: remote origin already exists” when running the above command. Two months after graduating, I found my dream job that aligned with my values and goals in life!" "Career Karma entered my life when I needed it most and quickly helped me match with a bootcamp. We’ll create a new Git repository, make a README.md file, and commit that file to the repository. Let’s initialize a new local repository on our machine. This Git command is commonly run after you have cloned a repository or when you are creating a new repository. You can use git remote add to add a remote to a Git repository. This will make their code accessible to all the collaborators on a project. Once a developer has finished making changes to a repository, they can push it to the remote version. They can work on a project on their local computers without changing the main version of the project. Git is distributed, which means that many different developers can have their own copy of a project. Remotes are an essential part of the Git system. A remote repository could be hosted on GitHub, BitBucket, GitLab, or another version control platform. When you set a remote, you can push code to and pull code from a remote repository. , and you consent to receive offers and opportunities from Career Karma by telephone, text message, and email. Get Your Coding Bootcamp Sponsored by Your EmployerĬareer Karma matches you with top tech bootcampsĪccess exclusive scholarships and prep courses.Education Stipends for Coding Bootcamps.Best Coding Bootcamp Scholarships and Grants.Ultimate Guide to Coding Bootcamp Loans.Best Free Bootcamps and Coding Training.Best Online Coding Bootcamps and Courses.This kind of setup can be helpful if you're pulling in changes from the main branch of a project and then pushing any changes you make to a separate branch of your own, for example. This can be done with the following commands: $ git remote set-url $ git remote set-url -push Create new project (New Directory > R Package > name the package) and click also Create git repository This will build the package skeleton. This means you can actually set two different remote repositories for "origin", one for the push operation and one for fetch. In the output of the last command you may have noticed that there are actually two lines listed for the "origin" remote repository. Once you've added a remote to your repo you can then verify it with the -v flag: $ git remote -v You can also set these remotes as your default push or pull locations, shortening your Git commands even more.įor example, to add a remote origin to your repository, you would use the command like this: $ git remote add origin :scottwrobinson/camo.git The remote name is helpful for being able to reference this repository without having to type out the entire location. The command you'll want to use is git remote add, and is generally used in the following way: $ git remote add
#GIT ADD REMOTE ORGIN HOW TO#
In this short article I'll explain exactly how to do that. Either way, it's beneficial to associate a remote repository to your local one. Or you may just want to have a way to link your local Git repo with the remote one on GitHub. This is beneficial for when you want to pull in updates from someone else's fork of a project, for example. In the Git version control system you're able to push and pull code from any number of remote repositories.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
